NeuroNode Class Reference
#include <NeuroNode.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| NeuroNode (const CylBase &cb, unsigned int parent, const vector< unsigned int > &children, unsigned int startFid_, Id elecCompt, bool isSphere) | |
| NeuroNode (Id elecCompt) | |
| NeuroNode () | |
| unsigned int | parent () const |
| unsigned int | startFid () const |
| Id | elecCompt () const |
| bool | isDummyNode () const |
| bool | isSphere () const |
| bool | isStartNode () const |
| const vector< unsigned int > & | children () const |
| void | addChild (unsigned int child) |
| void | clearChildren () |
| void | setParent (unsigned int parent) |
| void | setStartFid (unsigned int f) |
| double | calculateLength (const CylBase &parent) |
| void | findConnectedCompartments (const map< Id, unsigned int > &nodeMap, const vector< NeuroNode > &nodes) |
| void | innerTraverse (vector< NeuroNode > &tree, const vector< NeuroNode > &nodes, vector< unsigned int > &seen) const |
| void | setParentAndChildren (unsigned int index, int dendParent, vector< NeuroNode > &nodes, const map< Id, unsigned int > &dendMap) |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static unsigned int | removeDisconnectedNodes (vector< NeuroNode > &nodes) |
| static unsigned int | findStartNode (const vector< NeuroNode > &nodes) |
| static void | traverse (vector< NeuroNode > &nodes, unsigned int start) |
| static void | buildTree (vector< NeuroNode > &nodes, vector< ObjId > elist) |
| static void | buildSpinyTree (vector< ObjId > &elist, vector< NeuroNode > &nodes, vector< Id > &shaftId, vector< Id > &headId, vector< unsigned int > &spineParent) |
| static void | filterSpines (vector< NeuroNode > &nodes, vector< Id > &shaftId, vector< Id > &headId, vector< unsigned int > &parent) |
Detailed Description
Helper class for the NeuroMesh. Defines the geometry of the branching neuron.
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
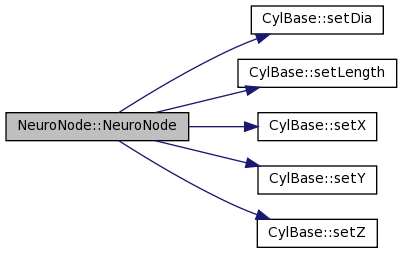
| NeuroNode::NeuroNode | ( | const CylBase & | cb, | |
| unsigned int | parent, | |||
| const vector< unsigned int > & | children, | |||
| unsigned int | startFid_, | |||
| Id | elecCompt, | |||
| bool | isSphere | |||
| ) |
This function explicitly fills in all fields of the NeuroNode
| NeuroNode::NeuroNode | ( | Id | elecCompt | ) |
This builds the node using info from the compartment. But the parent and children have to be filled in later
References CylBase::setDia(), CylBase::setLength(), CylBase::setX(), CylBase::setY(), CylBase::setZ(), and y.
| NeuroNode::NeuroNode | ( | ) |
Empty constructor for vectors
Member Function Documentation
| void NeuroNode::addChild | ( | unsigned int | child | ) |
Fills in child vector
Referenced by NeuroMesh::insertSingleDummy().
| static void NeuroNode::buildSpinyTree | ( | vector< ObjId > & | elist, | |
| vector< NeuroNode > & | nodes, | |||
| vector< Id > & | shaftId, | |||
| vector< Id > & | headId, | |||
| vector< unsigned int > & | spineParent | |||
| ) | [static] |
This function takes a list of elements that include connected compartments, and constructs a tree of nodes out of them. The generated nodes vector starts with the soma, and is a depth-first sequence of nodes. This is meant to be insensitive to vagaries in how the user has set up the compartment messaging, provided that there is at least one recognized message between connected compartments.
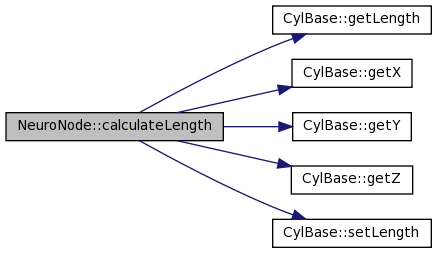
| double NeuroNode::calculateLength | ( | const CylBase & | parent | ) |
Calculates and returns compartment length, from parent xyz to self xyz. Assigns own length as a side-effect.
References CylBase::getLength(), CylBase::getX(), CylBase::getY(), CylBase::getZ(), and CylBase::setLength().
| const vector< unsigned int > & NeuroNode::children | ( | ) | const |
| void NeuroNode::clearChildren | ( | ) |
Zeroes out the child vector
Referenced by NeuroMesh::insertSingleDummy().
| Id NeuroNode::elecCompt | ( | ) | const |
| static void NeuroNode::filterSpines | ( | vector< NeuroNode > & | nodes, | |
| vector< Id > & | shaftId, | |||
| vector< Id > & | headId, | |||
| vector< unsigned int > & | parent | |||
| ) | [static] |
Trims off all spines from tree. Does so by identifying a set of reasonable names: shaft, head, spine, and variants in capitals. Having done this it builds two matching vectors of vector of shafts and heads, which is a hack that assumes that there are no sub-branches in spines. The returned nodes vector has non spine/shaft compartments only. The returned shaftId vector has all the shaft compartments. The returned headId vector has all the shaft compartments. The returned parent vector has the indices of the parent node for each shaft. There should be exactly the same number of entries in the shaftId, headId and parent vectors.
| void NeuroNode::findConnectedCompartments | ( | const map< Id, unsigned int > & | nodeMap, | |
| const vector< NeuroNode > & | nodes | |||
| ) |
Finds all the compartments connected to current node, put them all into the 'children' vector even if they may be 'parent' by the messaging. This is because this function has to be robust enough to sort this out
| static unsigned int NeuroNode::findStartNode | ( | const vector< NeuroNode > & | nodes | ) | [static] |
Find the start node, typically the soma, of a model. In terms of the solution, this should be the node at the root of the tree. Returns index in nodes vector. Technically the matrix solution could begin from any terminal branch, but it helps to keep the soma identical to the root of the tree.
Uses two heuristics to locate the start node: Looks for the node with the largest diameter, and also looks for node(s) with 'soma' in their name. If these disagree then it goes with the 'soma' node. If there are many of the soma nodes, it goes with the fattest.
| void NeuroNode::innerTraverse | ( | vector< NeuroNode > & | tree, | |
| const vector< NeuroNode > & | nodes, | |||
| vector< unsigned int > & | seen | |||
| ) | const |
Helper recursive function for traversing nodes to build tree.
| bool NeuroNode::isDummyNode | ( | ) | const |
True when this is a dummy node to represent the coordinates of the start end of a compartment. For example, the start coords of a compartment sitting on a spherical soma, or the start coords of a spine neck along a longer dendritic compartment. In all other cases the start coordinates are just those of the end of the parent compartment.
When the isDummyNode is true, the elecCompt represents the Id of the compartment whose start it is.
References CylBase::getNumDivs().
Referenced by NeuroMesh::getAdx(), NeuroMesh::nearest(), NeuroMesh::updateCoords(), and NeuroMesh::vGetVoxelMidpoint().

| bool NeuroNode::isSphere | ( | ) | const |
| bool NeuroNode::isStartNode | ( | ) | const |
| unsigned int NeuroNode::parent | ( | ) | const |
| static unsigned int NeuroNode::removeDisconnectedNodes | ( | vector< NeuroNode > & | nodes | ) | [static] |
Go through nodes vector and eliminate entries that have zero children, that is, are not connected to any others. Need to clean up 'children_' list after this is called.
| void NeuroNode::setParent | ( | unsigned int | parent | ) |
Assigns parent node info
Referenced by NeuroMesh::insertSingleDummy().
| void NeuroNode::setParentAndChildren | ( | unsigned int | index, | |
| int | dendParent, | |||
| vector< NeuroNode > & | nodes, | |||
| const map< Id, unsigned int > & | dendMap | |||
| ) |
| void NeuroNode::setStartFid | ( | unsigned int | f | ) |
Assignes startFid
| unsigned int NeuroNode::startFid | ( | ) | const |
| static void NeuroNode::traverse | ( | vector< NeuroNode > & | nodes, | |
| unsigned int | start | |||
| ) | [static] |
Traverses the nodes list starting from the 'start' node, and sets up correct parent-child information. This involves removing the identified 'parent' node from the 'children_' vector and assigning it to the parent_ field. Then it redoes the entire nodes vector (with due care for indexing of children and parents) so that it is in the correct order for a depth-first traversal. This means that you can take any entry in the list, and the immediately following entries will be all the descendants, if any.
The documentation for this class was generated from the following files:
- mesh/NeuroNode.h
- mesh/NeuroNode.cpp
 1.6.1
1.6.1